04 Nov
Introduction
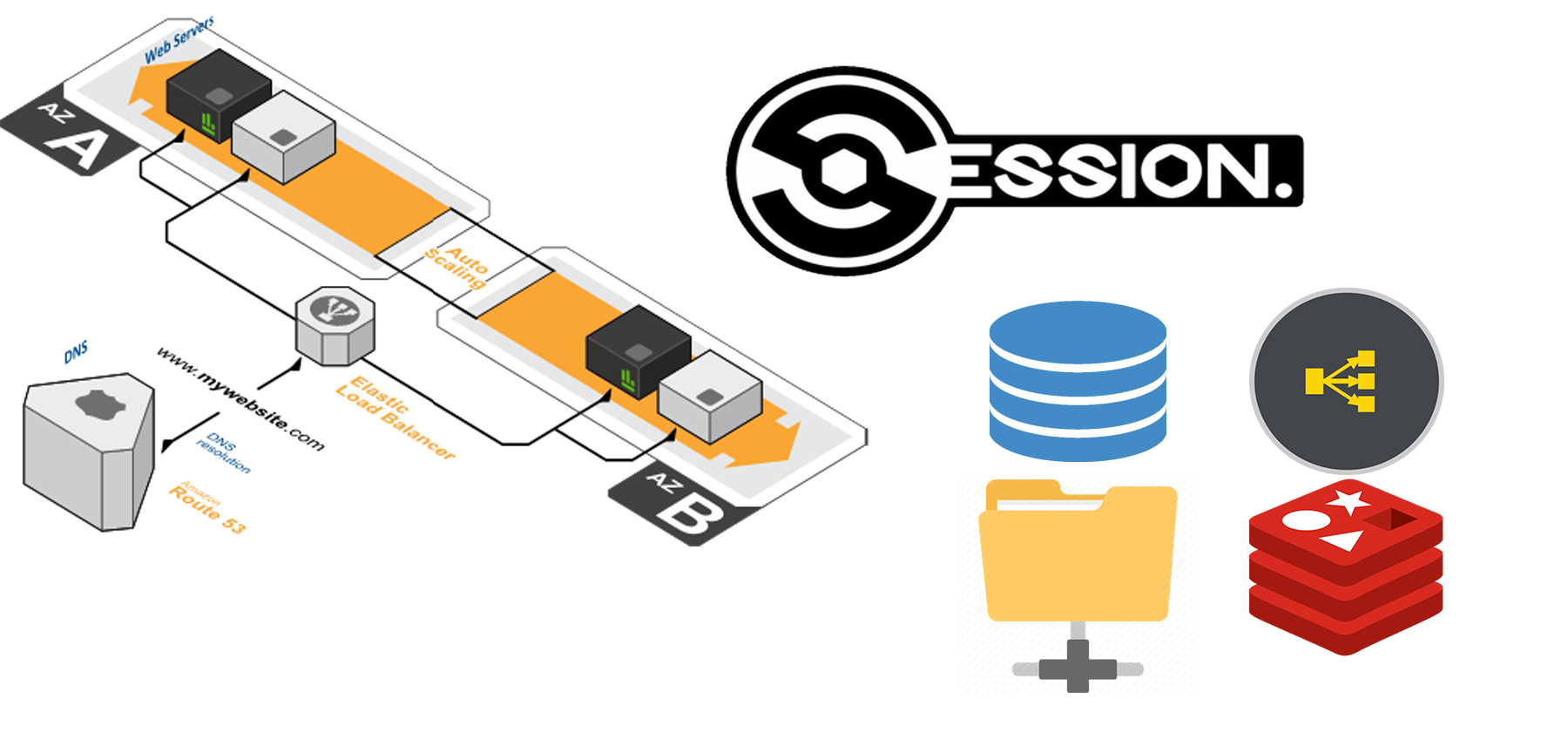
One of the common issues we ran into when running an application on a multi-server environment is how to manage sessions. especially an AWS auto-scaling architecture.
In this article, we’re going to discuss some approaches we used in our manage environments to overcome such issues.
Load Balancer Session Stickness:
AWS application load balancer “ELB” has a nice feature by offering session stickiness, with this feature the load balancer will ensure the same visit will be redirected to the same server on each request, and thus no need to distribute the session on all servers.
PROS:
- Easy Setup: just enable session stickiness and define lifetime on the load balancer.
- Application Independence: no additional customization needed and this is sometimes needed for legacy applications or applications you cant customize.
CONS:
- Round robin queue won’t work in an efficient way and some servers may have a higher load than others, and the autoscaling mechanism won’t be optimized.
Centralized Session Management:
from the title, we conclude that we need to store sessions in one location that can be accessed and shared across all servers.
Elastic File System:
 EFS is network storage that can be mounted on ec2 or even on-premise servers, it supports parallel mounting which is a powerful feature the standard NFS servers do not support.
EFS is network storage that can be mounted on ec2 or even on-premise servers, it supports parallel mounting which is a powerful feature the standard NFS servers do not support.
so the idea will be defining session files to be saved on one location and access by all servers, in PHP applications, for example, you can define the session storage file by using the session_save_path function.
PROS:
- Easy Setup: just enable session stickiness and define lifetime on the load balancer.
- Application Independence: no additional customization needed and this is sometimes needed for legacy applications or applications you cant customize.
CONS:
- Latency: accessing files is slower than EBS file system because it’s using NFS protocol.
Database:
Some applications support session management in database natively like Magento, and since the database is centralized storage for all application servers. this will give us centralized storage management.
PROS:
- Fast: accessing sessions inside the database is much faster than EFS.
CONS:
- Application Support: this feature requires native support by the application.
Elastic Cache:

This is our favorite and recommended method to handle sessions, and it can be achieved aby Memcache or Redis
PROS:
- Super Fast: accessing session data is so quick because these are in-memory databases.
- Can work with or without Application support: many frameworks and platforms support Redis or Memcache session management natively, even you can configure it on engine level, for example in PHP:
session.save_handler = redis session.save_path = tcp://127.0.0.1:6379
CONS:
- Additional cost: you will need to pay for the elastic cache as additional service.
Conclusion:
There are a few ways to handle sessions, we highly recommend using Redis or Memcache for session management for the reasons we demonstrated above, even its an additional cost, you can use these services in parallel for caching and reducing the load on the database,